BLOG
Thyroid Cancer: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
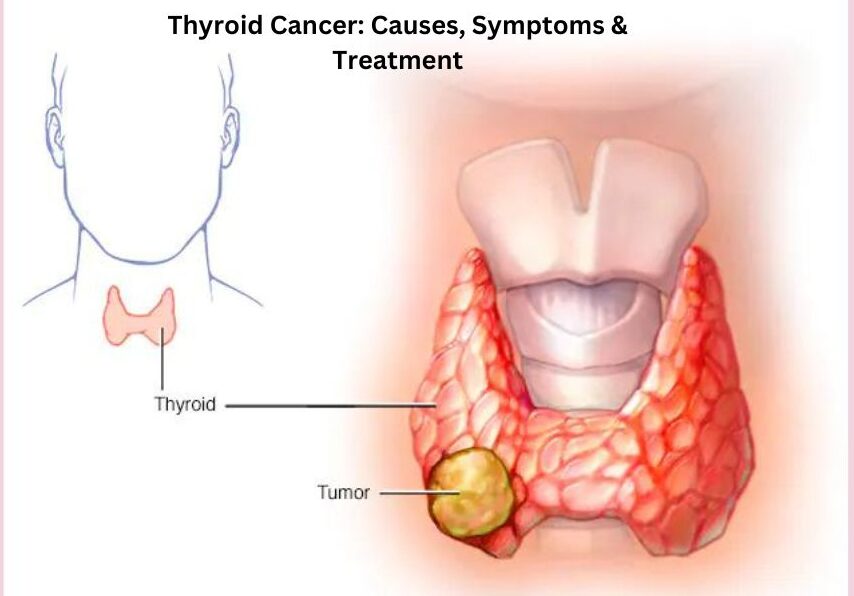
Thyroid cancer, a type of cancer that forms in the thyroid gland, is becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide. Though considered among the less aggressive cancers, its rising incidence calls for a deep dive into its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. This article explores the intricate details of thyroid cancer, aiming to educate and provide clarity on its management and the best medicine options available today.
What is Thyroid Cancer?
The thyroid gland, located at the base of your neck, plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism, heart function, digestion, and mood by producing thyroid hormones. Thyroid cancer occurs when the cells in the thyroid gland grow uncontrollably. It's important to note that the prognosis for thyroid cancer is typically very good, especially when diagnosed early.
Causes of Thyroid Cancer
While the exact cause of thyroid cancer remains unclear, several risk factors have been identified:
1. Genetic Factors:
Genetic mutations play a critical role in many cases of thyroid cancer. For example, mutations in the BRAF or RET genes are often found in certain types of thyroid cancers.
2. Radiation Exposure:
Exposure to radiation, particularly during childhood, significantly increases the risk. This includes radiation from medical treatments and environmental exposure.
3. Iodine Deficiency:
Though more commonly linked to benign thyroid conditions, iodine deficiency can sometimes influence thyroid cancer development.
4. Gender and Age:
Thyroid cancer is more common in women than men and typically occurs in people aged 30 to 60.
5. Family History:
Having a family history of thyroid cancer increases one's risk. Familial conditions like familial medullary thyroid cancer (FMTC) and Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2) are associated with higher risks.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as it progresses, certain symptoms can appear:
- A lump or swelling in the neck: This is the most common symptom.
- Pain in the neck and sometimes in the ears: Pain that persists and is not due to an infection or cold.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing: The growth of the tumor might press on the esophagus or trachea.
- Hoarseness or voice changes: This occurs if the cancer impacts the nerves connected to the voice box.
Diagnosing Thyroid Cancer
Diagnosis typically involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: Checking for noticeable lumps on the neck.
- Blood Tests: To assess thyroid function and look for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test helps to visualize the structure of the thyroid gland and detect nodules.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: Taking a sample from the thyroid nodule to examine for cancer cells.
- Radiographic Tests: Such as CT scans or MRIs to see if the cancer has spread.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Cancer
The treatment of thyroid cancer depends on the type, size, stage of the cancer, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment options include:
1. Surgery:
Most cases involve surgery to remove the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). If the cancer is diagnosed early, only part of the thyroid may need to be removed.
2. Radioactive Iodine Treatment:
This treatment uses radioactive iodine to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue after surgery and is very effective at targeting cancer cells that surgery might miss.
3. Thyroid Hormone Therapy:
After thyroidectomy, patients usually require life-long thyroid hormone replacement therapy to perform the functions previously carried out by the thyroid.
4. External Radiation Therapy:
This may be used if the cancer has spread to parts of the body where surgery is not feasible.
5. Chemotherapy:
This is less commonly used but may be necessary for aggressive types of thyroid cancer that don’t respond to other treatments.
6. Targeted Therapy:
For advanced thyroid cancers, targeted therapies like Sorafenib or Lenvatinib might be used. These drugs specifically target cancer cell mechanisms and help stop their growth.
Best Medicine for Thyroid Cancer
The "best" medicine depends significantly on the type and stage of thyroid cancer, as well as individual patient factors. Radioactive iodine treatment is highly effective for differentiated thyroid cancers, while targeted therapies are reserved for more advanced or resistant forms of thyroid cancer.
In conclusion, thyroid cancer, despite being cancer, often carries a good prognosis. Awareness of its causes, vigilant recognition of its symptoms, early and accurate diagnosis, along with appropriate and personalized treatment, are key to managing and overcoming this disease. Regular check-ups and following the treatment plan prescribed by oncology specialists are essential steps towards a successful recovery. If you suspect any symptoms or have a family history of thyroid issues, consulting with a healthcare provider will provide the best course of action tailored to your health needs. More

