BLOG
PARP Inhibitors: A Breakthrough in Cancer Treatment
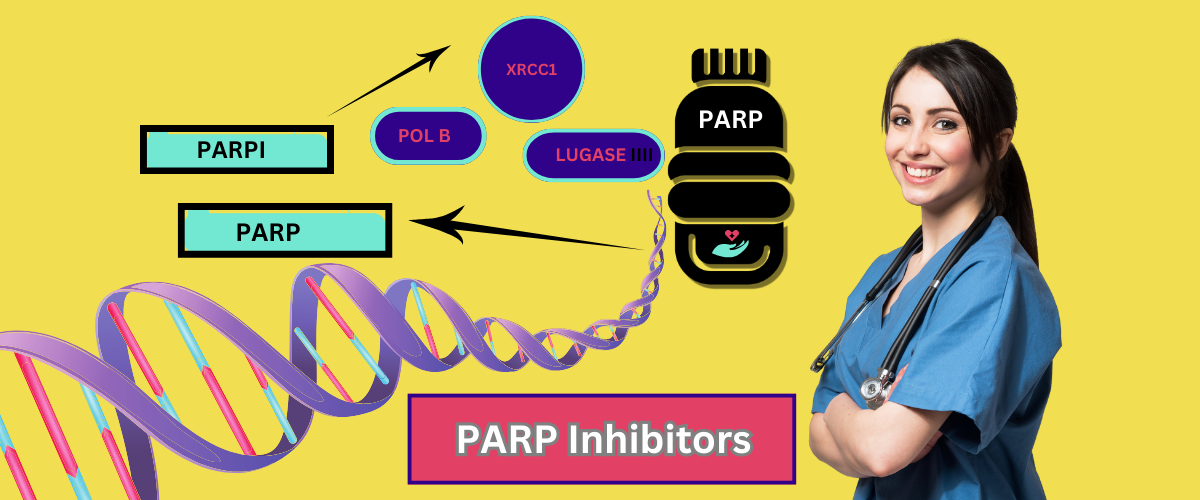
In recent years, the landscape of cancer treatment has undergone significant changes with the introduction of innovative therapies. One such groundbreaking class of drugs is PARP inhibitors. These drugs have garnered attention for their potential to revolutionize the way we approach cancer treatment, particularly for patients with specific genetic mutations. In this blog, we'll dive into what PARP inhibitors are, how they work, and why they're making waves in the medical community.
What Are PARP Inhibitors?
PARP inhibitors are a class of drugs designed to target and inhibit the activity of a protein called poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). PARP is involved in the repair of DNA damage, and its role is crucial in maintaining the integrity of our genetic material. When DNA becomes damaged, PARP helps to fix these breaks and prevent cell death. By inhibiting PARP, these drugs effectively disrupt the repair process, leading to the death of cancer cells that rely heavily on this repair mechanism.
How Do PARP Inhibitors Work?

To understand how PARP inhibitors work, it’s helpful to know a bit about the DNA repair process. Our cells are constantly exposed to various sources of DNA damage, including radiation, chemicals, and even errors during DNA replication. Cells have several mechanisms to repair this damage, one of which involves PARP. When DNA breaks occur, PARP attaches molecules called ADP-ribose to the damaged site, recruiting other repair proteins to fix the problem.
In cancer cells, particularly those with specific genetic mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2, the DNA repair machinery is often compromised. These mutations make it harder for cells to repair DNA damage effectively. PARP inhibitors exploit this weakness by further impairing the cell's ability to repair DNA. This leads to the accumulation of DNA damage, ultimately causing cancer cell death while sparing normal, healthy cells.
Why Are PARP Inhibitors Important?
PARP inhibitors have emerged as a promising treatment option for certain types of cancers, especially those associated with BRCA mutations. Here’s why they’re considered important:
1. Targeted Therapy: Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which can affect both cancerous and healthy cells, PARP inhibitors offer a more targeted approach. They specifically target cancer cells with faulty DNA repair mechanisms, reducing damage to normal cells and minimizing side effects.
2. Effective for BRCA-Mutated Cancers: BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes responsible for repairing damaged DNA. Mutations in these genes are linked to an increased risk of breast, ovarian, and other cancers. PARP inhibitors have shown remarkable efficacy in treating cancers associated with BRCA mutations, offering hope for patients who previously had limited options.
3. Potential for Combination Therapy: PARP inhibitors are being explored in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Combining these therapies can potentially enhance treatment effectiveness and overcome resistance mechanisms.
Notable PARP Inhibitors and Their Uses
Several PARP inhibitors have been approved for clinical use, each with its own set of indications and benefits:
1. Olaparib (Lynparza): One of the first PARP inhibitors to be approved, Olaparib is used to treat ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers with BRCA mutations. It has shown significant promise in improving progression-free survival in patients with these cancers.
2. Rucaparib (Rubraca): Approved for use in ovarian cancer patients with BRCA mutations, Rucaparib works similarly to Olaparib, targeting cancer cells’ inability to repair DNA effectively.
3. Niraparib (Zejula): Niraparib is used for ovarian cancer treatment and is notable for its effectiveness regardless of BRCA status. It offers another option for patients with advanced ovarian cancer.
4. Talazoparib (Talzenna): This PARP inhibitor is used for breast cancer treatment, particularly in patients with BRCA mutations. It has demonstrated potent efficacy in shrinking tumors and improving patient outcomes.
Benefits and Side Effects
Benefits:
- Increased Survival Rates: Clinical trials have shown that PARP inhibitors can significantly increase progression-free survival for patients with BRCA mutations and other DNA repair deficiencies.
- Improved Quality of Life: Because they target cancer cells more precisely, PARP inhibitors often lead to fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Side Effects:
- Common Side Effects: These can include nausea, fatigue, anemia, and loss of appetite. Most side effects are manageable and typically less severe than those associated with traditional chemotherapy.
- Serious Side Effects: In rare cases, PARP inhibitors can lead to severe side effects such as blood disorders or risk of secondary cancers. Regular monitoring is essential to manage these risks.
The Future of PARP Inhibitors
The field of cancer treatment is evolving rapidly, and PARP inhibitors are at the forefront of this change. Ongoing research is exploring their use in other cancers and in combination with other therapies. As our understanding of genetic mutations and cancer biology improves, PARP inhibitors may become an integral part of a broader arsenal of cancer treatments.
(FAQ)
1. What are PARP inhibitors?
PARP inhibitors are a class of drugs designed to block the activity of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) enzyme. This enzyme is involved in repairing DNA damage in cells. By inhibiting PARP, these drugs prevent cancer cells from repairing their damaged DNA, leading to their death while sparing healthy cells.
2. How do PARP inhibitors work?
PARP inhibitors target cancer cells that have faulty DNA repair mechanisms, particularly those with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. In normal cells, PARP helps repair DNA breaks. When PARP is inhibited, cancer cells with compromised DNA repair systems cannot fix their DNA damage, leading to their death.
3. Who can benefit from PARP inhibitors?
PARP inhibitors are especially beneficial for patients with cancers that have specific genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. They are commonly used to treat ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers associated with these mutations. However, research is expanding their use to other types of cancers and genetic profiles.
4. What types of cancers are treated with PARP inhibitors?
PARP inhibitors are primarily used for:
- Ovarian cancer (especially with BRCA mutations)
- Breast cancer (particularly in patients with BRCA mutations)
- Prostate cancer (associated with BRCA mutations)
- Some other cancers with specific genetic profiles
5. What are the most common PARP inhibitors?
Some of the most well-known PARP inhibitors include:
- Olaparib (Lynparza)
- Rucaparib (Rubraca)
- Niraparib (Zejula)
- Talazoparib (Talzenna)
6. What are the benefits of PARP inhibitors?
The benefits of PARP inhibitors include:
- Targeted Treatment: They specifically target cancer cells with defective DNA repair mechanisms, leading to fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
- Increased Survival Rates: They have been shown to improve progression-free survival in patients with certain genetic mutations.
- Quality of Life: Patients often experience a better quality of life due to reduced side effects.
7. What are the common side effects of PARP inhibitors?
Common side effects can include:
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Loss of appetite
8. Are there any serious side effects associated with PARP inhibitors?
In rare cases, serious side effects may occur, such as:
- Blood disorders (e.g., severe anemia or low platelet counts)
- Risk of secondary cancers
Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is important to manage these potential risks.
9. How are PARP inhibitors administered?
PARP inhibitors are typically administered orally in the form of tablets or capsules. The dosage and frequency depend on the specific drug and individual patient needs.
10. Can PARP inhibitors be used in combination with other treatments?
Yes, PARP inhibitors are often used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy, to enhance effectiveness and overcome resistance mechanisms. This combination approach is being actively researched to improve patient outcomes.
11. How can I find out if PARP inhibitors are right for me?
To determine if PARP inhibitors are a suitable treatment option, your healthcare provider will evaluate your specific cancer type, genetic mutations, and overall health. Genetic testing may be conducted to identify mutations that could make you a candidate for PARP inhibitor therapy.
12. What is the future of PARP inhibitors?
The future of PARP inhibitors looks promising as research continues to expand their use. Ongoing studies are exploring their effectiveness in other cancers, combinations with other therapies, and ways to reduce potential side effects. As our understanding of cancer genetics and treatment evolves, PARP inhibitors are likely to play an increasingly important role in personalized cancer therapy.
conclusion
PARP inhibitors represent a significant advancement in the fight against cancer. By specifically targeting cancer cells with defective DNA repair mechanisms, they offer a more focused and potentially less harmful treatment option. With continued research and development, these drugs hold promise for improving outcomes and providing new hope to patients battling cancer.
-
 Asviia Injection
Asviia Injection
₹22,401.00Original price was: ₹22,401.00.₹16,100.00Current price is: ₹16,100.00. -
 Bdpazo 400mg Tablet
Bdpazo 400mg Tablet
₹3,510.00Original price was: ₹3,510.00.₹2,850.00Current price is: ₹2,850.00. -
 Bevacirel 400mg Injection
Bevacirel 400mg Injection
₹56,889.56Original price was: ₹56,889.56.₹12,500.00Current price is: ₹12,500.00.
The Evolution of Cancer Treatments: A Journey from Ancient Remedies to Modern Innovations
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Overcoming Financial Challenges Associated with Cancer Treatment
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Innovative Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Treatment
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
National Walking Day: Step Up for Your Health
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
The Role of Immunotherapy in Modern Cancer Treatment
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Top 5 Cancer Hospitals in Uttarakhand
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
The Future of Cancer Research Emerging Trends and Breakthroughs
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Top 5 Cancer Hospitals in Tripura
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Top 5 Breast Cancer Medicines: Your Guide to Effective Treatments
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Top 5 Cancer Hospitals in Mizoram
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
Overcoming Cancer Drug Resistance: Strategies & Solutions
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments
The Cost of Chemotherapy in Delhi
-
Posted by
admin
- 0 comments