BLOG
Prostate Cancer – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment in India

Introduction
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern worldwide, particularly for men over the age of 50. In India, it is the second most common cancer among men, with a rising incidence in recent years. Understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring treatment options are crucial for effectively combating this disease. This blog aims to delve into the intricacies of prostate cancer, focusing on its causes, symptoms, and available treatments in the Indian context.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
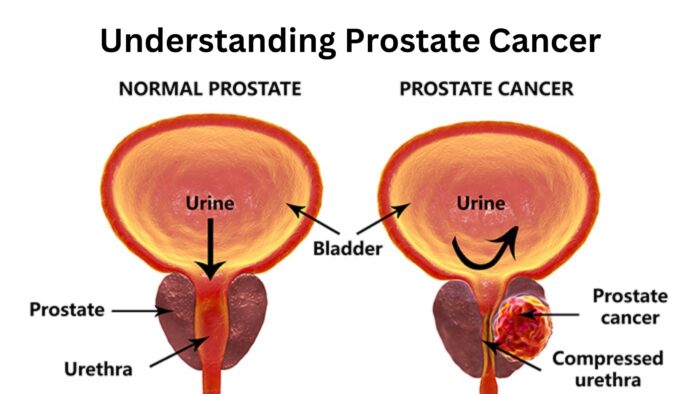
The prostate is a small gland located beneath the bladder, playing a vital role in the male reproductive system. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. While the exact cause of prostate cancer remains unclear, several factors contribute to its development.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
- Age: Advancing age is a significant risk factor for prostate cancer. Men over the age of 50 are at a higher risk, with the incidence increasing with age.
- Genetics: Family history and genetics play a crucial role in prostate cancer risk. Men with a family history of the disease are more likely to develop it themselves.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African American men, have a higher incidence of prostate cancer compared to others.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a high-fat diet may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer often does not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may manifest
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or maintaining a urine stream
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Erectile dysfunction
It is important to note that these symptoms can also indicate other prostate conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. Therefore, consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and evaluation is essential
These Medicine Uses For Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Diagnosis and Screening
Early detection of prostate cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes. In India, screening for prostate cancer typically involves a digital rectal examination (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. If abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic tests such as a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) and prostate biopsy may be recommended.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prostate cancer in India depends on various factors, including the stage of the disease, the patient's overall health, and personal preferences. Common treatment modalities include
- Active Surveillance: For low-risk prostate cancer, active surveillance may be recommended, involving regular monitoring of the disease without immediate treatment.
- Surgery: Surgical options for prostate cancer include radical prostatectomy, where the entire prostate gland is removed, or minimally invasive procedures such as robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy.
- Radiation Therapy: External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and brachytherapy are commonly used radiation techniques to target and destroy cancer cells in the prostate.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy aims to reduce the levels of male hormones (androgens) in the body, as they can fuel the growth of prostate cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: In advanced or metastatic prostate cancer, chemotherapy drugs may be used to slow the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs such as sipuleucel-T (Provenge) work by stimulating the body's immune system to attack cancer cells.
Access to Treatment in India
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer in India. Leading cancer hospitals and healthcare facilities across the country offer state-of-the-art infrastructure and expertise for managing prostate cancer. Moreover, the availability of generic medications and relatively lower treatment costs make prostate cancer treatment more accessible to a wider population.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite progress in prostate cancer care, several challenges persist in India, including awareness gaps, limited access to screening facilities in rural areas, and the stigma associated with discussing prostate-related issues. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community organizations to promote early detection, improve access to quality care, and enhance public awareness about prostate cancer
Conclusion
Prostate cancer remains a significant public health concern in India, affecting thousands of men each year. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and accessing timely treatment are paramount in effectively combating this disease. With advancements in medical technology and increased awareness, there is hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for prostate cancer patients in India. Regular health check-ups, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking prompt medical attention for any concerning symptoms are essential steps in the fight against prostate cancer.

